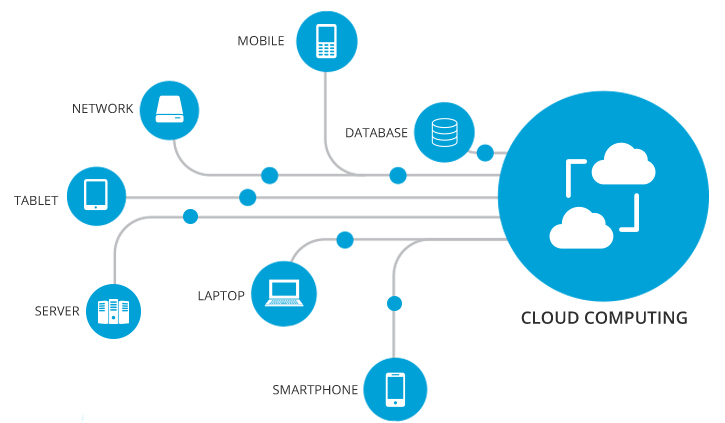
Cloud Computing is ubiquitous in modern technology infrastructure, as it offers on-demand availability, data storage resources (cloud storage), and computing power directly over the Internet. Cloud virtualizes server resources and converts hardware into services, allowing software companies and corporations to utilize them without worrying about hardware-related complexities.
Familiarizing Yourself With Cloud Computing Services
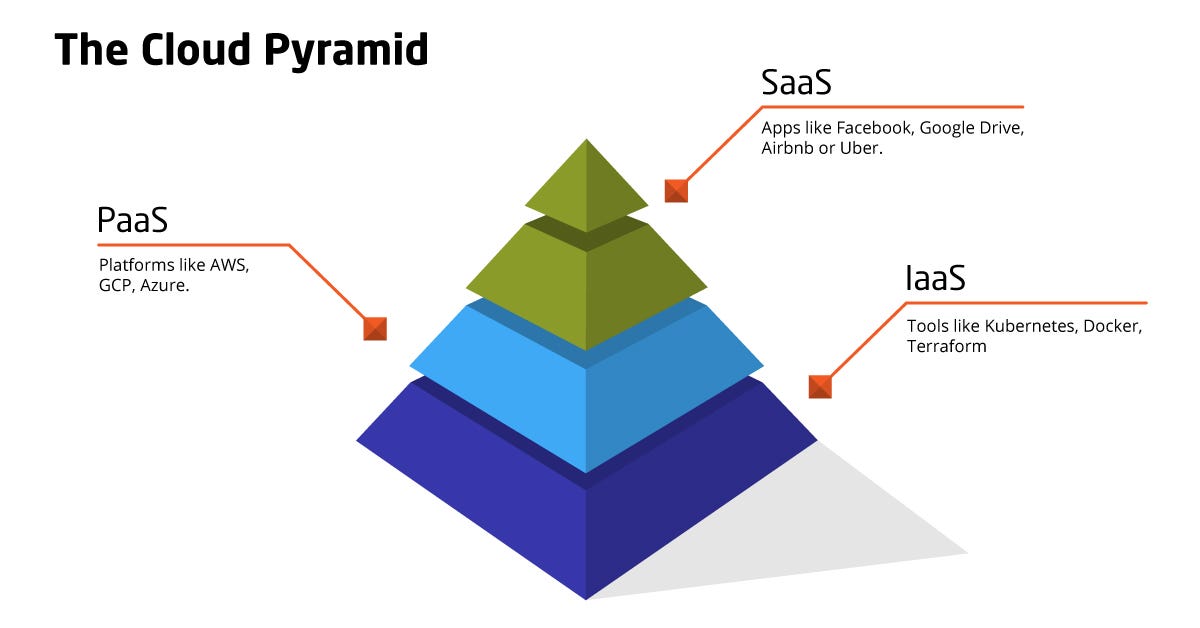
While more and more companies increasingly rely on cloud computing for everyday tasks, the methods in which they utilize them are by no means the same. In fact, there are many models of services that are offered through cloud computing service providers, with three of the main services being Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS).
In this article, we’ll take a closer look at these primary cloud computing services, as well as overview containers and the various cloud computing practices.
A Quick Overview: Infrastructure as a Service
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) serves to replace infrastructure used by typical businesses with cloud-accessible infrastructure. For example, if you had a series of server racks used to store important data for your business, you could move all of that information online, making it remotely accessible, by using IaaS. The benefit? You no longer have to worry about managing, setting up, or investing in the hardware systems needed for said storage and you can put more time and energy into your business itself.
A Quick Overview: Platform as a Service
Platform as a Service (PaaS) serves to provide users with even more defined tech that does not need to be set up, by offering a platform in which developers can dive right into developing, testing, and deploying new and customized software applications. While you are given less control over the system as a whole, this narrowed scope allows you to focus more on getting straight to the task on hand. The ease of access to these utilities allows for software development teams to boost productivity.
A Quick Overview: Software as a Service
Software as a Service or SaaS is the final form of services offered by cloud computing service providers and arguably the most prevalently used. In the SaaS model, third-party vendors deliver software to users typically on a subscription fee via the internet. One well-known use of a SaaS service is by Netflix, which uses AWS to provide a video streaming service over the internet to millions every day. The importance of cloud computing in this specific situation is that your computer doesn’t need to download anything! Rather, all it needs is a stable and strong internet connection that allows your computer to access Netflix’s cloud structure to binge the latest and greatest in film.
Understanding Additional Cloud Computing Services
In addition to these three core services (IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS), many more services are on the rise, especially Serverless Architecture that utilizes Backend as a Service (BaaS) and Function as a Service (FaaS).
This architecture setup makes cloud computing even more straightforward for users by eliminating their need to control, run, and manage any servers (hence “serverless”). Serverless cloud computations referred to as cloud functions, offer users a wide range of possibilities from video encoding to recognizing user-drawn shapes. Since cloud functions (FaaS) only charge users based off the consumption of compute resources, companies are easily able to scale to match user demand.
A Quick Overview of Cloud Containers and How They Work
Another important aspect of cloud computing lies in the employment of containers, which are highly portable, lightweight, and packaged applications. Cloud containers offer users increased flexibility by increasing possible application deployment environments. (This is similar to how portable computers offered users the flexibility to work from different locations.)
Containers serve to further enhance the speed at which teams can work by making it easier to transfer information through the cloud in a very lightweight manner.
Cloud computing also offers a variety of advantages over previous on-site computer structures. One of the most valuable advantages is the opportunity for rapid growth, achieved through the scalability and elasticity offered by cloud services.
Need for an expansion? Simply up your subscription with the provider or select additional necessary cloud services, and you’re ready to go in minutes. The idea that infrastructure can be built upon or drawn back instantaneously offers businesses a refined form of horizontal scaling far superior to traditional methods. This enhances profitability based on a pay-as-you-grow model, which is easy to adjust scale based on current demands. Why prolong growth by wasting time on building and setting up new hardware infrastructure on-site?
Finding the Right Cloud Solution for Your Business
While cloud computing is very enticing, there are certain details and specifics that companies need to look at when searching for and deciding on a cloud solution.
Cloud users must consider whether the convenience of not having to worry about on-site hardware is worth the risk of full reliance on cloud service providers to take care of issues. For example, imagine if AWS just disappeared tomorrow? Would Netflix be gone forever? Probably not! The company knows that a complete reliance on cloud services for all of their data, information, etc., offers a high risk of data loss and the possibility of data-migration headaches. As such, it’s wise for businesses to take on healthy cloud computing practices, like investing in on-site storage backups or diversifying the use of cloud service providers.
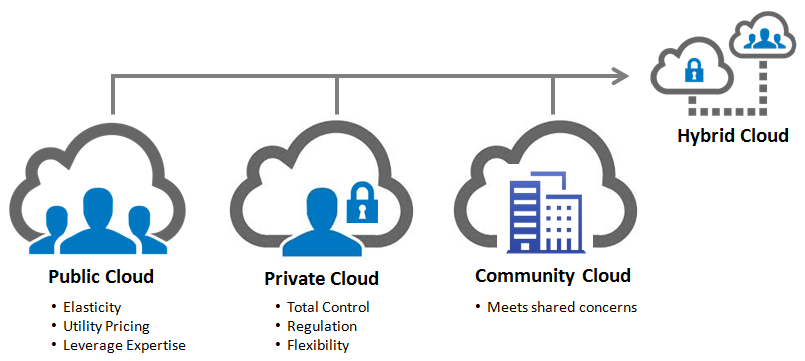
It’s also important to note that there are also different cloud computing services available to consumers, including public, private, and hybrid clouds.
Types of Cloud Computing Services Available to Consumers
Public Clouds
Public clouds offer users a shared network space of cloud access, giving multiple tenants access to the same services. The benefits of public clouds lie in the idea that the provider fully manages upkeep, leaving users without worry. Public clouds are also relatively cheap and scalable at subscription pricing, allowing individuals to use and pay for only what they need. Since public clouds consist of a myriad of shared resources, it is essential to be aware of the sensitivity of data, which can be transmitted through this type of network. Users should ensure that public cloud security measures match the standards they must follow.
Private Clouds
Private Clouds differ because the computer systems used are often constructed on-premise (sometimes still available through cloud service providers) and made available to a single individual, company, or organization through a private network. While significantly more expensive to set up and keep running, private clouds offer users enhanced security and increased customizable control. However, dedicated on-site cloud data centers require proper management and attention to remain effective and efficient.
Hybrid Clouds
Hybrid clouds attempt to spread services between both private and public clouds in an intelligent fashion to keep sensitive information secure on a private cloud, meanwhile allowing general computing and application services to remain cheap and widely accessible on a public cloud. This strategy enables users to keep all aspects of their cloud infrastructure running as efficiently as possible. However, keeping everything streamlined under a hybrid cloud setup can get tricky.
Utilize Cloud-Enabled Scalability With Confidence
Identifying the right strategy and services for your cloud computing needs can be difficult without the right help. At Golden Section, we offer full-service to software companies by fully leveraging the cloud to deliver and deploy the aforementioned software systems. Both the actual software (code) and the infrastructure to deliver the software are important parts of the equation. We utilize cloud-enabled scalability along with the elasticity and customizability of software to provide the highest level of B2B SaaS solutions.